A successful democratic revolution may well need a relatively wealthy and educated population, however, one of the main things that seem to drive revolutions themselves is just how many young adults there are in a country.
… countries in which 60 percent or more of the population is under the age of 30 are more likely to experience outbreaks of civil conflict than those where age structures are more balanced.
— Madsen (2011): The Demographics of Revolt
When there are lots of young people getting to the age when they are just trying to find jobs and start families, but the country’s economy can’t grow fast enough to provide all the jobs they need, then you have a lot of dissatisfied, disaffected people with time on their hands; it’s a tinderbox ready for any spark.
I recently attended a talk by Jennifer Scuibba where she laid out the case. Scuibba’s blog, also has a
a very good set of links that look at the age demographics of the current revolutions in the Arab world.
One of the links goes to a report by Richard Cincotta and others (Cincotta et al., 2003) that used this type of demographic analysis to figure out which countries were most likely to end up in conflict.
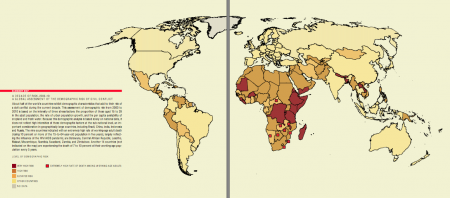
They talk about the demographic transition, “a population’s shift from high to low rates of birth and death,” as being a key factor in reducing the likelihood of conflicts. Therefore, they suggest:
… a range of policies promoting small, healthy and better educated families and long lives among populations in developing countries seems likely to encourage greater political stability
— Cincotta et al., 2003: The Security Demographic – Population and Civil Conflict After the Cold War
If civil conflict leads to a successful democratic transition, then political stability is probably not a net benefit.
However, once there is a democratic revolution, the same large cohort of young people still exists, which could make a country like Egypt unstable for quite a while, until it goes through the demographic transition. After all:
…countries do not become mature democracies overnight. They usually go through a rocky transition, where mass politics mixes with authoritarian elete politics in a volatile way. Statistical evidence covering the past two centuries shows that in this transitional phase of democratization, countries become more aggressive and war-prone, not less …
— Mansfield and Snyder (1995): Democratization and War