Utterly amazing. Keith Loutit’s Small Worlds Project, uses time-lapse photographs, carefully adjusted focus, and color highlighting to create videos that look like a lot like claymation animations.
Tag: time-lapse photography
Microscope photography!!!
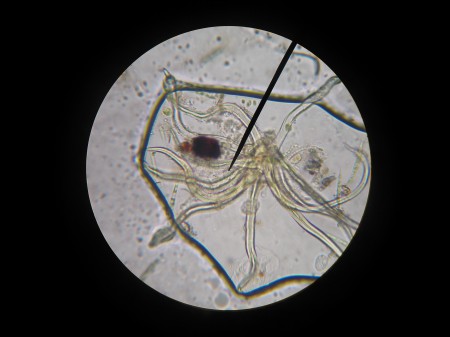
Did you know that if you hold up a regular digital camera up to the eyepiece of a microscope you can take a great picture of a magnified slide! I didn’t. And I really didn’t think it would work when I tried it, but the results are remarkable. With a somewhat steady hand you can also make decent animations.

I’ve never been very good at identifying things (I’m a lumper not a splitter) so all I think I can say for sure is that there are algae and protozoans in the picture. BiologyCorner has a nice identification guide for organisms usually found in ponds, which is part of one of their lessons, Biodiversity of Ponds.
Integrating Eyjafjallajökull

Current events often generate the teachable moments we’re always seeking in order to strike students’ imagination. The eruption of Eyjafjallajökull is a prime example. I’ve already used it to point out the intersection of geothermal energy and plate tectonics, but there is so much more.

Eyjafjallajökull has been a wonderful subject for the art of photography. The image above is a great example but the time-lapse photos have been excellent. The photo to the right captures not just the stars streaking across the sky with a three minute exposure but the fiery red arcs of the volcanic ejecta.

One of the major benefits of the space program so far has been its Earth observing satellites. There is so much going on in the image to the left that it’s hard to know where to start. Why are there all those clouds over Iceland? (warmer land mass creates convection); what’s with the two plumes from the volcano, one concentrated high level and one disperse low level plume; fjords on the upwind side of the island and the straightened coastline on the lee; greenish plumes of glacier-ground, rock flour discharging into the ocean.

The dinosaurs were done in either by an asteroid impact in the Yucatan or the eruption of the massive flood volcanoes in Deccan, India, or quite probably both. Both of these events launched an enormous amount of ash, gas and fine particles into the upper atmosphere, blocking sunlight, causing global cooling. Well the ash from Eyjafjallajökull and the sulfur dioxide gas may be having a similar effect on Europe, and if there’s enough of it, on the world. The 1992 eruption of Mt. Pinatubo cooled the globe by about half a degree Celsius.
Snowfall
To accurately observe nature sometimes takes time. Land-labs are intended to get students out into nature for a week at a time throughout the entire year so that they can see the change in the seasons. But sometimes you need to winnow things down, speed things up, to observe the slow changes that you just miss. Time-lapse photography is one great way to do this.