Energy cannot be either created or destroyed, just changed from one form to another. That is one of the fundamental insights into the way the universe works. In physics it’s referred to as the Law of Conservation of Energy, and is the basic starting point for solving a lot of physical problems. One great example is calculating the average temperature of the Earth, based on the balance between the amount of energy it receives from the Sun, versus the amount of energy it radiates into space.
The Temperature of Radiation
Anything with a temperature that’s not at absolute zero is giving off energy. You right now are radiating heat. Since temperature is a way of measuring the amount of energy in an object (it’s part of its internal energy), when you give off heat energy it lowers your body temperature. The equation that links the amount of radiation to the temperature is called the Stefan-Boltzman Law:
![]()
where:
ER = energy radiated (W/m-2)
T = temperature (in Kelvin)
s = constant (5.67 x 10-8 W m-2 K-4)
Now if we know the surface area of the Earth (and assume the entire area is radiating energy), we can calculate how much energy is given off if we know the average global temperature (the radius of the Earth = 6371 km ). But the temperature is what we’re trying to find, so instead we’re going to have to figure out the amount of energy the Earth radiates. And for this, fortunately, we have the conservation of energy law.
Energy Balance for the Earth
Simply put, the amount of energy the Earth radiates has to be equal to the amount of energy gets from the Sun. If the Earth got more energy than it radiated the temperature would go up, if it got less the temperature would go down. Seen from space, the average temperature of the Earth from year to year stays about the same; global warming is actually a different issue.
So the energy radiated (ER) must be equal to the energy absorbed (EA) by the Earth.
![]()
Now we just have to figure out the amount of solar energy that’s absorbed.
Incoming Solar Radiation
The Sun delivers 1367 Watts of energy for every square meter it hits directly on the Earth (1367 W/m-2). Not all of it is absorbed though, but since the energy in solar radiation can’t just disappear, we can account for it simply:
- Some if the light energy just bounces off back into space. On average, the Earth reflects about 30% of the light. The term for the fraction reflected is albedo.
- What’s not reflected is absorbed.
So now, if we know how many square meters of sunlight hit the Earth, we can calculate the total energy absorbed by the Earth.
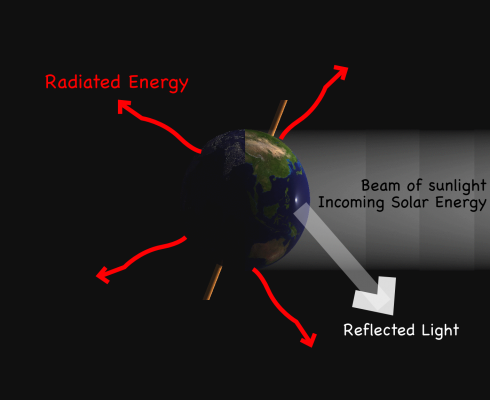
With this information, some algebra, a little geometry (area of a circle and surface area of a sphere) and the ability to convert units (km to m and celcius to kelvin), a student in high-school physics should be able to calculate the Earth’s average temperature. Students who grow up in non-metric societies might want to convert their final answer into Fahrenheit so they and their peers can get a better feel for the numbers.
What they should find is that their result is much lower than that actual average surface temperature of the globe of 15 deg. Celcius. That’s because of how the atmosphere traps heat near the surface because of the greenhouse effect. However, if you look at the average global temperature at the top of the atmosphere, it should be very close to your result.
They also should be able to point out a lot of the flaws in the model above, but these all (hopefully) come from the assumptions we make to simplify the problem to make it tractable. Simplifications are what scientists do. This energy balance model is very basic, but it’s the place to start. In fact, these basic principles are at the core of energy balance models of the Earth’s climate system (Budyko, 1969 is an early example). The evolution of today’s more complex models come from the systematic refinement of each of our simplifications.
Advanced Work
If students do all the algebra for this project first, and then plug in the numbers they should end up with an equation relating temperature to a number of things. This is essentially a model of the temperature of the Earth and what scientists would do with a model like this is change the parameters a bit to see what would happen in different scenarios.
Feedback
Global climate change might result in less snow in the polar latitudes, which would decrease the albedo of the earth by a few percent. How would that change the average global temperature?
Alternatively, there could be more snow due to increased evaporation from the oceans, which would mean an increase in albedo …
This would be a good chance to talk about systems and feedback since these two scenarios would result in different types of feedback, one positive and one negative (I’m not saying which is which).
Technology / Programming
Setting up an Excel spreadsheet with all the numbers in it would give practice with Excel, make it easier for the student to see the result of small changes, and even to graph changes. They could try varying albedo or the solar constant by 1% through 5% to see if changes are linear or not (though they should be able to tell this from the equation).
A small program could be written to simulate time. This is a steady-state model, but you could assume a certain percent change per year and see how that unfolds. This would probably be easier as an Excel spreadsheet, but the programming would be useful practice.
Of course this could also be the jumping off point for a lot of research into climate change, but that would be a much bigger project.
References
Yochanan Kushnir has a page/lecture that treats this type of zero-dimesional, energy balance model in a little more detail.








